Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morohashi, Yuko; Suzuki, Satoshi
JAEA-Technology 2014-045, 116 Pages, 2015/03
The failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) system collects the tagging gas that migrates into the reactor cover gas from a failed pin. The tagging gas is made of stable isotopes of Kr and Xe. The isotopic composition of the tagging gas can be made specific to each assembly. The assembly containing a failed fuel pin can be identified by analyzing the isotopic composition. The FFDL system is comprised of two tagging gas concentration devices. The concentration rate is designed to be higher than 200. Past examinations demonstrated that the concentration rate meets the requirement with a noble gas concentration of 1ppm. However, the actual noble gas concentration emitted from a failed fuel is assumed to be much lower. In the present study, the performance of FFDL system was investigated by measuring low concentration gas of the actual fuel failure level. As a result, the concentration rate was confirmed to be more than tens of thousands, which sufficiently satisfies the design demand.
Iguchi, Tetsuo; Watanabe, Kenichi*; *; Nose, Shoichi; Harano, Hideki;
JNC TY9400 2000-019, 34 Pages, 2000/05
None
Aoyama, Takafumi;
PNC TN9420 96-058, 27 Pages, 1996/10
This report introduces the nuclear instrumentation system and the major radiation measurement techniques used in the Experimental Fast Reactor "JOYO". In the introduction of the nuclear instrumentation system, system function and role as reactor plant equipment, specifications and characteristics of neutron detectors, and layout of the system are described. Reactor dosimetry was used to evaluate neutron dose and their spectra for various irradiation tests and surveilance tests performed in JOYO. The multiple-foil activation method which is currently used and the Helium Accumulation fluence Monitor (HAFM) under development are described. The fuel failure detection (FFD) and the failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) systems in which radiation measurement plays a key role are introduced. It was shown some of the major experimental results obtained from a series of fuel failure simulation tests performed in JOYO. Finally, as a new radiation measurement technique, the Plastic Scintillation Fiber (PSF) is described which is a position sensitive radiation detector that can detect the radiation dose rate at the relevant position in the fiber. The PSF is used to upgrade the gamma-ray distribution measurement to accurately evaluate the Corrosion Products (CPs) behavior in the JOYO primary coolant system.
Sumino, Kozo; Aoyama, Takafumi; Nagai, Akinori
PNC TN9410 96-216, 85 Pages, 1996/07
The cover gas radioactivity in the reactor vessel increases when a fuel pin failure occurs or RTCB (Run to Cladding Breach) testing is performed. The activity must be reduced to minimize the personnel exposure and to maintain the reserve capacity of the waste gas system in which the residual fission gas is stored. The CGCS (Cover Gas Cleanup System) was installed in the JOYO primary cover gas system to collect and remove the fission gas. The cryogenic charcoal bed cooled by the liquid nitrogen selectively adsorbs the krypton and xenon due to the adsorption ratio difference. The collection ratio for xenon and krypton was measured using fission gas in the fuel failure simulation test and a standard helium diluted non-radioactive gas. As a result, the collection ratio was confirmed to be more than 90% for xenon and more than 80% for krypton by six hours operation of CGCS. It was confirmed that the CGCS has a capability to remove the fission gas effectively.
Nogami, Yoshitaka; ; ; Seki, Masayuki; ; Tobita, Noriyuki; Nagai, Shuichiro
PNC TN8410 93-190, 93 Pages, 1993/03
None
Isozaki, Kazunori; ; Ito, Hideaki; ; Chatani, Keiji; ;
PNC TN9520 93-006, 198 Pages, 1992/11
None
Morimoto, Makoto; Okubo, Toshiyuki; ; ; ; ;
PNC TN9410 91-334, 64 Pages, 1991/10
An failed fuel detection and location system (FFDL) using a sipping method is adopted as the FFDL of Joyo. FFDL has not operated since the first falled fuel simulated (FFDL-I) test in April, 1985 because Joyo has not yet experienced any operation with breached fuels. Therefore, the operational test (II) of FFDL was carried out on July 12 19, 1991 for a preparation of the FFDL-II test which is scheduled in 1992. Main results from the test are as follows ; (1)The adequacy of the functions and operating procedure of FFDL was reaffirmed and the operating experience was gained. (2)Radioactivity measurement was conducted by FFDL for six subassemblies and their integrity was confirmed.
19, 1991 for a preparation of the FFDL-II test which is scheduled in 1992. Main results from the test are as follows ; (1)The adequacy of the functions and operating procedure of FFDL was reaffirmed and the operating experience was gained. (2)Radioactivity measurement was conducted by FFDL for six subassemblies and their integrity was confirmed.
; ; ; Tobita, Tsutomu; ; ; ; ; Yokouchi, Iichiro; ; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 34(1), p.567 - 570, 1987/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Hoken Butsuri, 22, p.189 - 207, 1987/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ;
JAERI-M 84-108, 38 Pages, 1984/06
no abstracts in English
Onda, Kaoru*; Yamaguchi, Katsuhisa
PNC TN952 83-08, 258 Pages, 1983/12
A Data processing program SISC0, which has capabilities of checking the information of experimental data measurements with little labor and of analyzing the data conveniently using the checked information, was developed to conduct the accurate data processing of the test results of low-flow and low-heat-flux sodium boiling runs and the other runs obtained from the experiments carried out with the Transient Sodium Boiling and Fuel Failure Propagation Test facility. It is devised to use, to the full extent, the utility libraries of the Interactive Data Analysis System AXEL installed in the FACOM M-190/200 computer system at the O-arai Engineering Center. The data managements of the SISCO code are composed of two sub-systems : one is the BSISCO having functions of creating or updating the data bases with batch jobs to prepare for subsequent data analyses, and another is the ISISCO which is in charge of analyzing the data with TSS job under the support of AXEL system. In onder to respond to various kinds of requirements from analysts, seven option routines and thirteen command-macro procedures are available in respective sub-systems. The SISCO code supports following two types of data handling jobs : (i)data calibration job ; to fix and service the information of measurements, which is to be compiled into a preservation data file for the data reproduction, by the statistical analyses of calibration data and the displays of the results, (ii)data analysis job ; to obtain the graphic outputs of the multi-data analyses applied to the specified preservation data files. The data analysis of the SISCO code is so designed that one can use a certain command-macro as a stand-alone utility program appliciable to any test data comprehensively. It is possible to yield (a) summary traces of the test results containing the sub-frames of time series data plots of key signals in one figure, (b) multi-traces of the axial temperatures at required transient times, (c) analytical ...
*; *; Aoi, Sadanori*
PNC TN941 82-74VOL1, 151 Pages, 1982/03
A study of hypothetical core disruptive accidents (HCDAs) in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju (714 MWt) has been conducted by using the SAS3D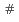 accident analysis code. A loss-of-flow (LOF) due to the loss of off-site power and a transient overpower (TOP) due to control assembly withdrawal, both at rated power, are considered as the HCDA initiators with a postulated total failure of the reactor shutdown system. The accident scenarios of each postulated anticipated transient without scram are studied for the three burnup stages of Monju: the beginning-of-initial cycle (BOIC) ; a beginning-of-equilibrium cycle (BOEC); and an end-of-equilibrium cycle (EOEC). The neutronics data used in this study has been obtained by a 3-dimensional HEX-Z diffusion code and the first order perturbation calculations. The reactivity coefficients used in this study are the design nominal values without taking into account their uncertainties. The nominal design value of the maximum positive sodium void worth in Monju is a relatively small value of 2.5$ in the EOEC core. In the 2 cents/sec TOP, the reactor power shows a sudden increase following the onset of FCIs (Molten-Fuel/Coolant Interactions) in high-powered fuel assemblies but the maximum power level reached is less than 5 times the rated power and due to the fuel sweepout negative reactivity in the FCI fuel assemblies, the reactor is shutdown within 0.1 sec at the latest after the first FCI onset. The extent of damaged fuel assemblies is largest in the clean (FP-gas free) BOIC core in which the radial power peaking is smaller than in BOEC and EOEC cores, and about 17% of the fuel assemblies are damaged in the central region of the core. In the equilibrium cycle cores the damage extents are limited to about 5% core-center assemblies and this is smaller than in the BOIC core because of the larger radial power peaking and the rapid fuel sweepout reactivity insertion accelerated by the FP-gas pressure in the ...
accident analysis code. A loss-of-flow (LOF) due to the loss of off-site power and a transient overpower (TOP) due to control assembly withdrawal, both at rated power, are considered as the HCDA initiators with a postulated total failure of the reactor shutdown system. The accident scenarios of each postulated anticipated transient without scram are studied for the three burnup stages of Monju: the beginning-of-initial cycle (BOIC) ; a beginning-of-equilibrium cycle (BOEC); and an end-of-equilibrium cycle (EOEC). The neutronics data used in this study has been obtained by a 3-dimensional HEX-Z diffusion code and the first order perturbation calculations. The reactivity coefficients used in this study are the design nominal values without taking into account their uncertainties. The nominal design value of the maximum positive sodium void worth in Monju is a relatively small value of 2.5$ in the EOEC core. In the 2 cents/sec TOP, the reactor power shows a sudden increase following the onset of FCIs (Molten-Fuel/Coolant Interactions) in high-powered fuel assemblies but the maximum power level reached is less than 5 times the rated power and due to the fuel sweepout negative reactivity in the FCI fuel assemblies, the reactor is shutdown within 0.1 sec at the latest after the first FCI onset. The extent of damaged fuel assemblies is largest in the clean (FP-gas free) BOIC core in which the radial power peaking is smaller than in BOEC and EOEC cores, and about 17% of the fuel assemblies are damaged in the central region of the core. In the equilibrium cycle cores the damage extents are limited to about 5% core-center assemblies and this is smaller than in the BOIC core because of the larger radial power peaking and the rapid fuel sweepout reactivity insertion accelerated by the FP-gas pressure in the ...
Uruga, Kazuyoshi*; Murakami, Tsuyoshi*; Sakamura, Yoshiharu*; Nakayoshi, Akira; Kitawaki, Shinichi; Kofuji, Hirohide
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Aizawa, Kosuke; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Okazaki, Hitoshi*; Hayashi, Masateru*
no journal, ,
FFD-DN (failed fuel detection system by delayed neutron monitoring) method is to measure the delayed neutron flux which is released from failed fuel to sodium coolant when fuel failure occurs. Here, the part of FFD-DN method will be cleared. Then, reactor trip before fuel failure propagation could be performed by new FFD-DN detection form with B C filter and collimator.
C filter and collimator.
Kato, Shinya; Morohashi, Yuko; Muto, Keitaro
no journal, ,
In order to confirm performance of MONJU failed fuel detection and location system (FFDL), confirmation of accuracy for identifying failed fuel will be conducted by using simulated tag gas.
Morohashi, Yuko; Higuchi, Tetsuo*; Ishii, Keisuke*; Kitamura, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English